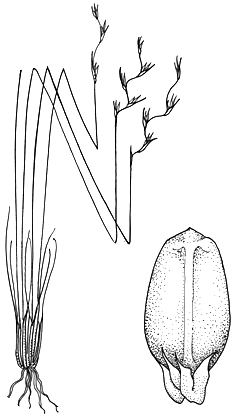
Description: Perennials, often with creeping rhizomes and clump-forming. Culms nodeless, compressed or terete.
Leaves basal; blade isobilateral, culm-like, or occasionally reduced to sheathing scales; ligule present.
Inflorescence panicle-like, simple or compound; involucral bracts usually shorter than inflorescence. Spikelets terete, with 1 bisexual flower (rarely 2) and usually 1 or more male flowers below it. Glumes 4–8, spirally arranged; lowest 2–4 empty, mostly shorter than upper fertile glumes; uppermost glume usually reduced. Hypogynous scales usually 6, rarely 3, basally inflated at maturity, often bristle-like and scabrous above, falling with nut. Stamens 3. Style 3-fid, continuous with ovary, persistent and fused with nut, shortly conical to pyramidal, acute to obtuse.
Nut trigonous to terete, crowned by paler style base, usually smooth at maturity but often irregularly wrinkled, with 3 pale ribs (not always obvious) extending from style base down sides of nut.
Distribution and occurrence: World: c. 70 species, Asia, Australia, New Zealand, New Caledonia. Australia: c. 65 species (c. 60 species endemic), all States except N.T.
Nuts vary little between species, but hypogynous scales can vary within one taxon, often bearing a bristle-like apical appendage.
Text by K. L. Wilson November 2005
Taxon concept: KL Wilson in Flora of NSW vol 4
Taxa not yet included in identification key
Lepidosperma prospectum,
Lepidosperma sieberi
| | Key to the species | |
| 1 | Culms terete, or compressed so as to be oval in cross section (with rounded margins), or 4-angled, or irregularly angular, sometimes grooved, or more or less biconvex with 1 flat acute margin and the other rounded to broad-acute (Lepidosperma semiteres) | 2 |
| Culms flat or concavo-convex or with 1 face convex, or biconvex with 2 clearly defined acute margins | 10 |
| 2 | Rachis strongly flexuous | 3 |
| Rachis straight or scarcely curved
Back to 1 | 4 |
| 3 | Leaf sheaths very dark red-brown to dark grey-brown, straw-coloured near apex; fertile glumes 8–11 mm long, scarcely longer than basal sterile glumes; nut 4–5 mm long; hypogynous scales 3, plus 3 swollen stamen filaments | Lepidosperma forsythii |
| Leaf sheaths straw-coloured to reddish; fertile glumes 7–9 mm long, to twice as long as the basal sterile glumes; nut 2.8–4 mm long; hypogynous scales 5 or 6, inflated; stamen filaments not swollen
Back to 2 | Lepidosperma filiforme |
| 4 | Spikelets in dense clusters, more or less appressed to central axis of more or less oblong inflorescence | 5 |
| Spikelets loosely arranged along more or less spike-like branches of inflorescence
Back to 2 | 7 |
| 5 | Culms 4-angled (strongly so at least in part) | Lepidosperma quadrangulatum |
| Culms terete or oval in cross section
Back to 4 | 6 |
| 6 | Culms terete but deeply to shallowly 1- or 2-grooved; nut with rounded fused style base | Lepidosperma neesii |
| Culms oval in cross section; nut with pyramidal fused style base
Back to 5 | Lepidosperma evansianum |
| 7 | Culms subterete with 1 acute, flat margin, or irregularly angular, or biconvex with 1 acute margin and 1 rounded; spikelets spreading | Lepidosperma semiteres |
| Culms terete or slightly compressed but without acute margins; spikelets appressed to spikelike branches
Back to 4 | 8 |
| 8 | Leaf sheaths blackish or very dark red-brown | Lepidosperma urophorum |
| Leaf sheaths straw-coloured, reddish, or orange-brown
Back to 7 | 9 |
| 9 | Leaf sheaths straw-coloured to reddish; spikelets 6–10 mm long; fertile glumes 7–9 mm long | Lepidosperma filiforme |
| Leaf sheaths orange-brown to red-brown; spikelets 4–5 mm long; fertile glumes c. 4 mm long
Back to 8 | Lepidosperma clipeicola |
| 10 | Culms rather spongy, compressible, strongly biconvex | Lepidosperma longitudinale |
| Culms tough, not or scarcely compressible, flat to biconvex
Back to 1 | 11 |
| 11 | Inflorescence with loosely arranged spikelets and/or small inflorescence with few spikelets | 12 |
| Inflorescence with more or less densely clustered, numerous spikelets
Back to 10 | 18 |
| 12 | Inflorescence 7–65 cm long, with long, more or less spreading branches | 13 |
| Inflorescence 0.8–8 cm long, spike-like or with short branches more or less appressed to main axis
Back to 11 | 15 |
| 13 | Culms with margins viscid, scabrous, often ciliate | Lepidosperma viscidum |
| Culms with margins scabrous or smooth but not viscid or ciliate
Back to 12 | 14 |
| 14 | Culms flat, or slightly convex on 1 face, or concavo-convex, 30–100 cm long, 2–8 mm wide | Lepidosperma laterale |
| Culms biconvex, or margins flat with central biconvex ridge, or strongly convex on 1 face and flat on the other, 70–180 cm long, 5–15 mm wide
Back to 13 | Lepidosperma elatius |
| 15 | Rachis flexuous | Lepidosperma tortuosum |
| Rachis straight or scarcely curved
Back to 12 | 16 |
| 16 | Leaves equalling or exceeding inflorescences (to twice as long) | Lepidosperma curtisiae |
| Leaves shorter than inflorescences
Back to 15 | 17 |
| 17 | Spikelets mostly 3.5–4 mm long; culms usually biconvex | Lepidosperma gunnii |
| Spikelets mostly 5–8.5 mm long; culms usually flat or concavo-convex
Back to 16 | Lepidosperma laterale |
| 18 | Inflorescence more or less ovate in outline with spreading ranches, 2–7 cm diam | 19 |
| Inflorescence more or less narrow-oblong in outline, with branches more or less appressed to central axis, 1–2 (rarely to 3) cm diam
Back to 11 | Lepidosperma limicola |
| 19 | Culms with central biconvex ridge and thin, broad, flattened margins, 5–20 mm wide | Lepidosperma gladiatum |
| Culms flat, concavo-convex, or convex on 1 face and flat on the other, 3–7 mm wide
Back to 18 | 20 |
| 20 | Culm margins scabrous to scaberulous, somewhat cutting; culms flat, concavo-convex, or convex on 1 face | Lepidosperma concavum |
| Culm margins smooth but cutting, often becoming erose with age; culms biconvex or convex on 1 face
Back to 19 | Lepidosperma latens |
|


