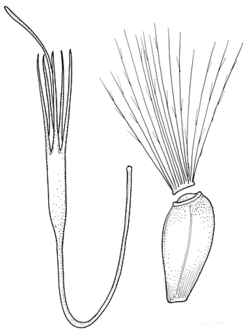
Description: Large perennial herbs, usually spinose.
Leaves a basal rosette (often withering at fruiting) and cauline, alternate, pinnatisect, with spiny segments.
Heads large, globose, terminal, solitary or in loose cymes of 2 or 3; involucral bracts several-seriate, unequal, leathery or fleshy, spine-tipped, glabrous, the outer and middle with a stout spine or an ovate to triangular appendage at the apex; receptacle convex, fleshy, with bristles. Florets all tubular, bisexual, fertile; 5-toothed, purplish, blue or white. Anthers caudate at base, apex subacute. Style branches linear, erect, appressed.
Achenes ovoid-pyramidal or obovoid-cylindrical, glabrous; pappus of numerous, several-seriate, plumose bristles united in a ring at the base.
Distribution and occurrence: World: 10 species, Mediterranean region. Australia: 2 species (naturalized), N.S.W., Vic., S.A., W.A.
Text by L. Murray
Taxon concept:
| | Key to the species | |
| 1 | Leaves with upper surface shortly tomentose, lower surface white-tomentose, with rigid yellow spines at apex and clustered at base and on each ultimate lobe; heads 4–5 cm diam., bracts leathery, often purplish | Cynara cardunculus |
| Leaves with upper surface glabrescent and lower surface grey-tomentose, not spinose, but with mucronate segments; heads 8–15 cm diam.; involucral bracts fleshy at base, usually green | Cynara scolymus |
|


